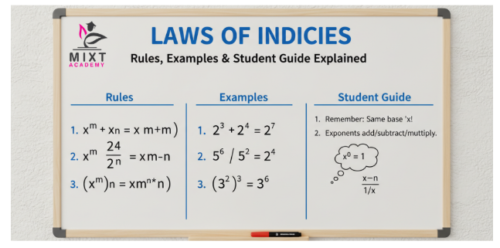

The more rules you know, the simpler the math expressions, and the easier mathematics becomes. One example is the laws of indices, which are among the first important algebraic concepts students learn. The laws of indices help students deal with a range of problems involving powers and exponents and teach them the building blocks of more complex mathematics.
Students who study online with Mixt Academy can build a strong understanding of indices, which helps them do better in algebra and succeed in GCSE and IGCSE maths. This guide explains the concept clearly, includes practical examples, and shows how students can apply these rules effectively.
What Are the Laws of Indices?
An index is simply a number that indicates how many times a number is multiplied by itself. The number in front is called the base and is the number that is multiplied, and the number written in the index (usually to the right and above) is called the exponent.
For example:
5^3 = 5 × 5 × 5 = 125
Here:
- 5 is the base
- 3 is the index
Knowing indices will help you in your algebra, scientific notation, and higher mathematics. Students studying the laws of indices in maths will apply these rules throughout their academic careers.
Why are the Laws of Indices Important?
The laws of indices help students to:
- Break down complicated algebraic problems
- Answer questions in less time
- Use scientific notation
- Understand the concepts of exponential increase and decrease
- Get ready for the GCSE, IGCSE and Further Maths exams.
Because indices are significant for developing valuable mathematical problem-solving skills, online tutoring platforms like Mixt Academy focus heavily on teaching them.
The Core Laws of Indices
The rules stated below are the most basic laws of indices. Depending on the level of the curriculum, students will most likely learn about the 8 laws of indices, 9 laws of indices, or even the 10 laws of indices, but any of these will be an extension of the basic rules that have been outlined.
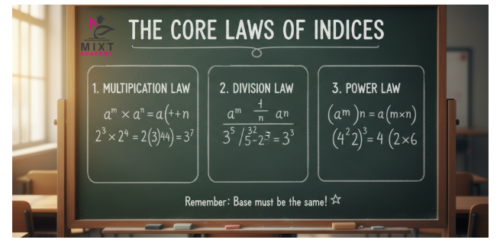
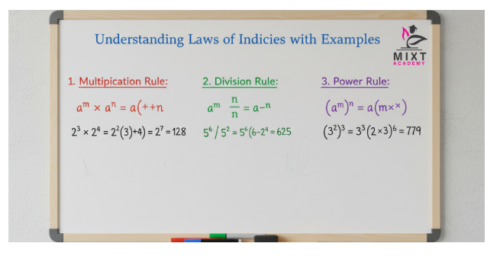
1. Multiplication Law
When multiplying powers with the same base, add the indices:
a^m × a^n = a^(m+n)
Example:
x^3 × x^4 = x^7
2. Division Law
When dividing powers with the same base, subtract the indices:
a^m ÷ a^n = a^(m−n)
Example:
y^8 ÷ y^3 = y^5
3. Power of a Power Law
When raising a power to another power, multiply the indices:
(a^m)^n = a^(mn)
Example:
(x^2)^3 = x^6
4. Zero Index Law
Any non-zero number raised to the power of zero equals 1:
a^0 = 1
Example:
7^0 = 1
5. Negative Index Law
A negative index means reciprocal:
a^(−n) = 1 / a^n
Example:
x^(−2) = 1 / x^2
6. Fractional Index Law
Fractional indices represent roots:
a^(1/2) = √a
Example:
16^(1/2) = 4
This rule is essential in understanding roots and powers together.
Understanding Laws of Indices with Examples
Examples are a great way for students to get a complete understanding of the law of indices.Students practising regularly through guided lessons, such as those offered by Mixt Academy, often develop confidence much faster.
Laws of Indices for Different Class Levels
Below is the overview of the law of indices for different class levels.
Laws of Indices Class 8
In class 8, students are expected to know and be able to:
- Use basic powers
- The multiplication law
- The division law
- The power of a power
This is the level that started building the groundwork for higher algebra.
List of Complete Extended Rules
Some versions of the curricula have extensions such as:
8 Laws of Indices & Laws of Indices
A clear educational infographic illustrating the 8 Laws of Indices, featuring all eight rules with colorful.
The 9 Laws of Indices and 10 Laws of Indices
These may also include:
- Separate product power rules
- Separate quotient power rules
- Expanded fractional power forms
The education board and curriculum influence these variations.
Common Mistakes Students Should Avoid
Students often commit the following mistakes when calculating the law of indices:

Learning through structured, one-on-one online lessons with Maths tutors at Mixt Academy helps students avoid these mistakes.
Practice Resources: Worksheets and PDFs
Students gain assisted learning and understanding through practice materials. Examples include:
- Laws of indices worksheet
- Laws of indices pdf
These practice materials are designed to reinforce understanding of the laws of indices. Worksheets typically include:
- Questions requiring simplification
- Fractional index
- Negative index
- Questions resembling real exam questions
Real-World Applications of the Law of Indices
The laws of indices are used in:
- Scientific notation
- Physics formulas
- Computer science
- Engineering calculations
- Financial growth models
This shows that indices go beyond school mathematics.
How Online Tutoring Helps Students Master Indices
Algebra is arguably one of the most challenging branches of mathematics for learners at all ages and levels. This is mostly due to the lack of a step-by-step guide to understanding the various concepts of algebra.

Online tutoring platforms such as Mixt Academy offer the following services to help students understand the law of indices:
- Expert Maths tutors
- Individual-based lesson plans
- Step-by-step interactive lesson plans
- Worksheets for independent work and memory retention
- Online tutoring for the preparation of exams
The structured approach of using online tutoring services to understand the law of indices is good for learners.
Final Thought
Learning the various laws of indices is important to succeeding in mathematics. These laws help to break down and simplify complex mathematical expressions. Understanding these laws prepares students to study algebra and more complex branches of mathematics. When students are provided the right tools, such as The Laws of Indices Worksheet and The Laws of Indices PDF Guide, coupled with consistent practice, they will succeed.
Online tutoring platforms such as Mixt Academy are effective in helping students to learn and understand the Law of Indices. Still, because of how they structure the online tutoring sessions, they help learners apply the concepts to real-life situations.
FAQs
What are the 7 laws of indices?
- First Index Law: am × an = am + n
- Second Index Law: am / an = am – n
- Third Index Law: a0 = 1 (where a ≠ 0)
- Fourth Index Law: (am)n = am × n
- Fifth Index Law: (a × b)m = am × bm
- Sixth Index Law: (a / b)m = am/bm
- Negative Indices: a-n = 1 / an (where a≠0)
- Square Roots: √a = a1/2
What is the rule of all indices?
Below are the rules of all indices:
- Rule one: Any constant or variable with an index of ‘0’ will be equal to one, no matter what the base value is.
- Rule two: Any negative index is shown as a reciprocal of the positive index of the same variable.
What does index 3 mean?
The word index means power. In the expression 5^3, 5 is the base, and 3 is the index. The plural form of index is indices. Indices indicate repeated multiplication, 5^3 = 5 5 5.
How can students improve their understanding of indices?
With more structured guidance, dedicated practice worksheets, and individualised one-to-one reasoning, students will learn the law of indices more quickly. Many students find specialised online tutoring the most informative, including platforms like Mixt Academy, where expert online tutors support students through the index laws and provide detailed practice related to the tests to build and solidify students’ knowledge and self-assurance.
What are the 7 laws of exponents in maths?
The 7 laws of exponents are:
- Product of Powers Law: am × an = a m+n.
- Quotient of Powers Law: am/an = a m-n.
- Power of a Power Law: (am)n = a mn.
- Power of Product Law: (ab)m = amb m.
- Power of Quotient Law: (a/b)m = am/b m.
- Zero Power Law: a0 = 1.
- Negative Exponent Law: a-m = 1/a m.